Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(13):5103-5122. doi:10.7150/ijbs.75410 This issue Cite
Review
Phase separation in Cancer: From the Impacts and Mechanisms to Treatment potentials
1. Hunan Key Laboratory of Cancer Metabolism, Hunan Cancer Hospital and the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China.
2. Hunan Key Laboratory of Translational Radiation Oncology, 283 Tongzipo Road, Changsha 410013, Hunan, China.
* Contributed equally
Abstract
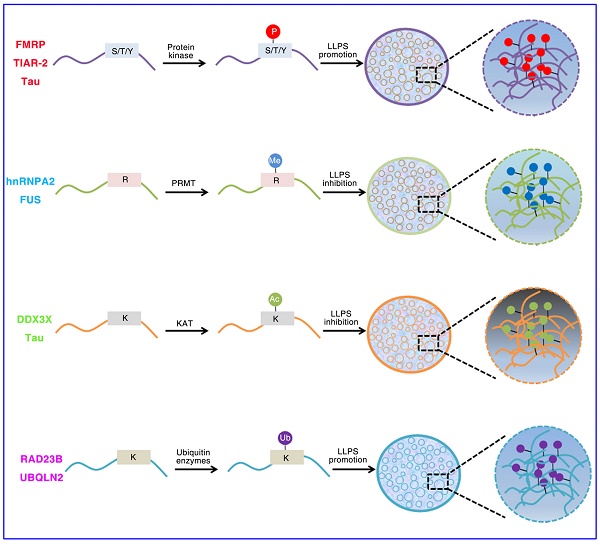
Cancer is a public health problem of great concern, and it is also one of the main causes of death in the world. Cancer is a disease characterized by dysregulation of diverse cellular processes, including avoiding growth inhibitory factors, avoiding immune damage and promoting metastasis, etc. However, the precise mechanism of tumorigenesis and tumor progression still needs to be further elucidated. Formations of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) condensates are a common strategy for cells to achieve diverse functions, such as chromatin organization, signal transduction, DNA repair and transcriptional regulation, etc. The biomolecular aggregates formed by LLPS are mainly driven by multivalent weak interactions mediated by intrinsic disordered regions (IDRs) in proteins. In recent years, aberrant phase separations and transition have been reported to be related to the process of various diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Herein, we discussed recent findings that phase separation regulates tumor-related signaling pathways and thus contributes to tumor progression. We also reviewed some tumor virus-associated proteins to regulate the development of virus-associated tumors via phase separation. Finally, we discussed some possible strategies for treating tumors by targeting phase separation.
Keywords: phase separation, cancer, biomolecular condensates, tumor-related signaling pathways, virus-associated tumors

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact