10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(15):5681-5697. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65044 This issue Cite
Review
Mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): pathomechanisms and pharmacotherapies
1. Department of Endocrinology, Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, Clinical Research Hospital of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Hefei), University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230001, China.
2. Department of Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, 230022, Anhui, China.
3. Department of Foundations of Medicine, New York University Long Island School of Medicine, Mineola, New York, NY 11501, USA.
4. School of Pharmacy, Pharmacy Australia Centre of Excellence, The University of Queensland, Woolloongabba, Queensland, 4102 Australia.
Abstract
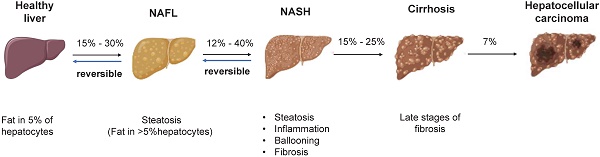
The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increases year by year, and as a consequence, NAFLD has become one of the most prevalent liver diseases worldwide. Unfortunately, no pharmacotherapies for NAFLD have been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration despite promising pre-clinical benefits; this situation highlights the urgent need to explore new therapeutic targets for NAFLD and for the discovery of effective therapeutic drugs. The mouse is one of the most commonly used models to study human disease and develop novel pharmacotherapies due to its small size, low-cost and ease in genetic engineering. Different mouse models are used to simulate various stages of NAFLD induced by dietary and/or genetic intervention. In this review, we summarize the newly described patho-mechanisms of NAFLD and review the preclinical mouse models of NAFLD (based on the method of induction) and appraises the use of these models in anti-NAFLD drug discovery. This article will provide a useful resource for researchers to select the appropriate model for research based on the research question being addressed.
Keywords: Drug discovery, mouse model, NAFLD, NASH, pharmacotherapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact