10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(1):294-310. doi:10.7150/ijbs.78097 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Direct targeting of sEH with alisol B alleviated the apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
1. College of Pharmacy, Second Affiliated Hospital, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, China.
2. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518061, China.
3. Department of Entomology and Nematology, UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California, Davis, CA 95616, United States.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
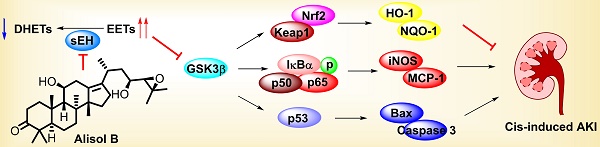
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a pathological condition characterized by a rapid decrease in glomerular filtration rate and nitrogenous waste accumulation during hemodynamic regulation. Alisol B, from Alisma orientale, displays anti-tumor, anti-complement, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its effect and action mechanism on AKI is still unclear. Herein, alisol B significantly attenuated cisplatin (Cis)-induced renal tubular apoptosis through decreasing expressions levels of cleaved-caspase 3 and cleaved-PARP and the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 depended on the p53 pathway. Alisol B also alleviated Cis-induced inflammatory response (e.g. the increase of ICAM-1, MCP-1, COX-2, iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α) and oxidative stress (e.g. the decrease of SOD and GSH, the decrease of HO-1, GCLC, GCLM, and NQO-1) through the NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways. In a target fishing experiment, alisol B bound to soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) as a direct cellular target through the hydrogen bond with Gln384, which was further supported by inhibition kinetics and surface plasmon resonance (equilibrium dissociation constant, KD = 1.32 μM). Notably, alisol B enhanced levels of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and decreased levels of dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids, indicating that alisol B reduced the sEH activity in vivo. In addition, sEH genetic deletion alleviated Cis-induced AKI and abolished the protective effect of alisol B in Cis-induced AKI as well. These findings indicated that alisol B targeted sEH to alleviate Cis-induced AKI via GSK3β-mediated p53, NF-κB, and Nrf2 signaling pathways and could be used as a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of AKI.
Keywords: Alisol B, acute kidney injury, cisplatin, soluble epoxide hydrolase, nephrotoxicity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact