10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(2):484-501. doi:10.7150/ijbs.78654 This issue Cite
Review
Novel Role of the SIRT1 in Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases
1. Department of Cardiology, Xi'an No.3 Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Northwest University. Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, Northwest University, Xi'an, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Resource Biology and Biotechnology in Western China, Ministry of Education. Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, Northwest University, Xi'an, China.
3. Department of General Surgery, Tangdu Hospital, The Airforce Medical University, 1 Xinsi Road, Xi'an 710038, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
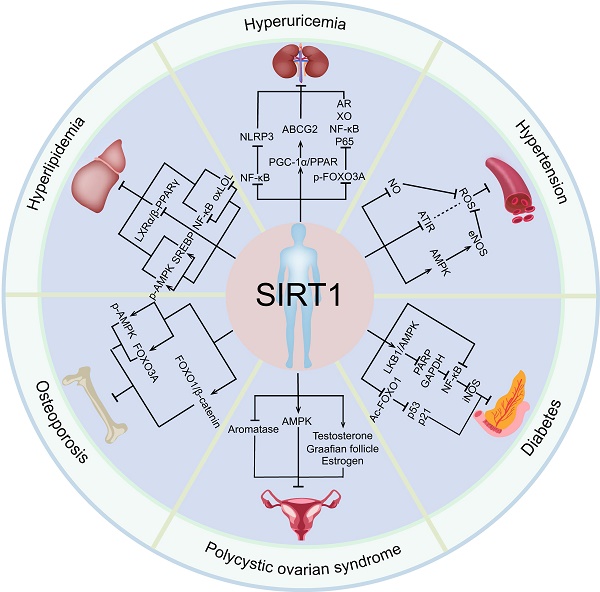
Silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1), a highly conserved NAD+-dependent deacetylase, is a cellular regulator that has received extensive attention in recent years and regarded as a sensor of cellular energy and metabolism. The accumulated evidence suggests that SIRT1 is involved in the development of endocrine and metabolic diseases. In a variety of organisms, SIRT1 regulates gene expression through the deacetylation of histone, transcription factors, and lysine residues of other modified proteins including several metabolic and endocrine signal transcription factors, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effects of endocrine and metabolic diseases. These evidences indicate that targeting SIRT1 has promising applications in the treatment of endocrine and metabolic diseases. This review focuses on the role of SIRT1 in endocrine and metabolic diseases. First, we describe the background and structure of SIRT1. Then, we outline the role of SIRT1 in endocrine and metabolic diseases such as hyperuricemia, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, osteoporosis, and polycystic ovarian syndrome. Subsequently, the SIRT1 agonists and inhibitors in the above diseases are summarized and future research directions are proposed. Overall, the information presents here may highlight the potential of SIRT1 as a future biomarker and therapeutic target for endocrine and metabolic diseases.
Keywords: SIRT1, endocrine metabolic, agonists, inhibitors

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact