10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(5):1455-1470. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79438 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CXCL14 promotes metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through ACKR2-depended signaling pathway
1. Department and Institute of Physiology, College of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei 11221, Taiwan.
2. Department of Nursing, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, and Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion Research Center, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Chiayi 61363, Taiwan.
3. Research Center for Industry of Human Ecology and Research Center for Chinese Herbal Medicine, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan 33303, Taiwan.
4. Department of Safety Health and Environmental Engineering, Ming Chi University of Technology, New Taipei City 24301, Taiwan.
5. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi 61363, Taiwan.
6. Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi 61363, Taiwan.
7. Graduate Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan 33302, Taiwan.
8. Center for Environmental Toxin and Emerging-Contaminant Research, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung 83347, Taiwan.
9. Super Micro Research and Technology Center, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung 83347, Taiwan.
10. Department of Respiratory Care, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Chiayi 61363, Taiwan.
11. School of Oral Hygiene, College of Oral Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan.
12. Translational Medicine Center, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei 11101, Taiwan.
13. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung 40402, Taiwan.
14. Department of Medical Research, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien 97002, Taiwan.
Abstract
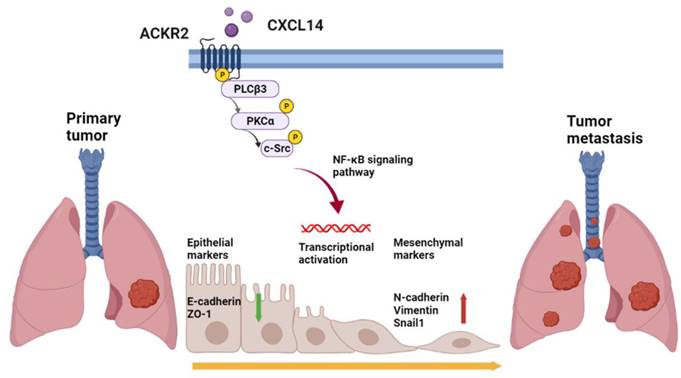
Background: Lung cancer is a malignant tumor with metastatic potential. Chemokine ligand 14 (CXCL14) has been reported to be associated with different cancer cell migration and invasion. However, few studies have explored the function of CXCL14 and its specific receptor in lung cancer metastasis. This study aims to determine the mechanism of CXCL14-promoted cancer metastasis.
Methods: The expression of CXCL14, atypical chemokine receptor 2 (ACKR2), and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers was evaluated by the public database of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), Western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Migration and wound healing assays were used to observe the motility of cancer cells. A luciferase reporter assay was performed to analyze transcription factor activity. The metastasis of lung cancer cells was evaluated in an orthotopic model.
Results: We have presented that overexpression of CXCL14 and ACKR2 was observed in lung cancer datasets, human lung tumor sections, and lung cancer cells. Furthermore, the migration of CXCL14-promoted lung cancer cells was determined in vitro and in vivo. In particular, ACKR2 knockdown abolished CXCL14-induced cancer cell motility. Additionally, ACKR2 was involved in CXCL14-triggered phospholipase Cβ3 (PLCβ3), protein kinase Cα (PKCα), and proto-oncogene c-Src signaling pathway and subsequently upregulated nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) transcription activity leading to EMT and migration of lung cancer cells. These results indicated that the CXCL14/ACKR2 axis played an important role in lung cancer metastasis.
Conclusion: This study is the first to reveal the function of CXCL14 in promoting EMT and metastasis in lung cancer. As a specific receptor for CXCL14 in lung cancer, ACKR2 mediates CXCL14-induced signaling that leads to cell motility. Our findings can be used as a prognostic biomarker of lung cancer metastasis.
Keywords: human lung cancer, CXCL14, ACKR2, metastasis, epithelial mesenchymal transition

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact