ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(7):2053-2066. doi:10.7150/ijbs.74123 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Gli1 promotes the phenotypic transformation of valve interstitial cells through Hedgehog pathway activation exacerbating calcific aortic valve disease
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China.
2. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
3. Hubei Engineering Technology Research Center of Chinese Materia Medica Processing, College of Pharmacy, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
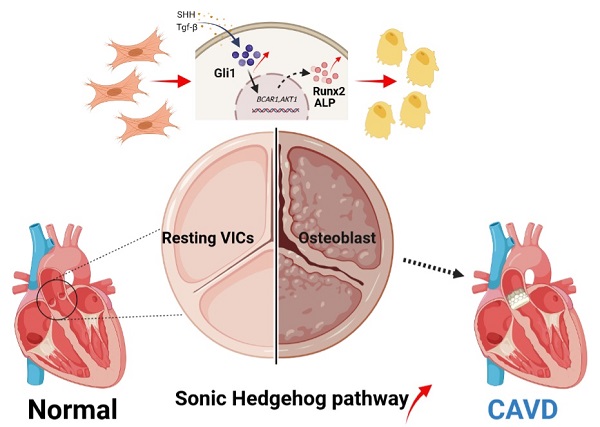
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is the most prevalent human valve disease worldwide. Multiple factors induce "irreversible" pathological changes in the aortic valve leaflets, resulting in changes in cardiac hemodynamics, eventually leading to heart failure. However, no effective pharmaceutical interventions have been found and prosthetic valve replacement is the only curative approach. Glioma-associated oncogene 1 (Gli1) exerts a regulatory role on cardiovascular diseases, and it is already a therapeutic target to combat tumors. Our research aimed to explore the role and basic mechanism of Gli1 in CAVD, to pave the way for the discovery of effective drugs in the treatment of CAVD. Human aortic valve tissues were obtained to evaluate Gli1 expression and primary valve interstitial cells (VICs) were used to perform related experiments. The results showed that Gli1 promoted cell proliferation and significantly accelerated cell osteogenic transformation through the up-regulation of the osteogenic factors Runx2 and Alp, in turn through the AKT signaling pathway by targeting P130cas expression. Furthermore, Gli1 was activated by TGF-β and sonic hedgehog through the canonical and non-canonical Hedgehog signaling pathways in VICs. Our results indicated that Gli1 promoted cell proliferation and accelerated cell osteogenic transformation in VICs, providing a new strategy for the therapy of CAVD by targeting Gli1.
Keywords: Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD), glioma-associated oncogene 1 (Gli1), Hedgehog signaling pathway, AKT signaling pathway, osteogenic transformation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact