ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(7):2097-2113. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81824 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Berberine inhibits high fat diet-associated colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiota-mediated lysophosphatidylcholine
1. Department of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, The Cancer Hospital of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Zhejiang Cancer Hospital), Institute of Basic Medicine and Cancer (IBMC), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310022, China.
2. Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Oncology Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022, China.
3. Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310053, China.
4. Dr. Neher's Biophysics Laboratory for Innovative Drug Discovery, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau, 999078, China.
5. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, The Second Hospital Affiliated to Air Force Medical University, Xi'an 710038, China.
6. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310003, China.
7. Key Laboratory of Head & Neck Cancer Translational Research of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
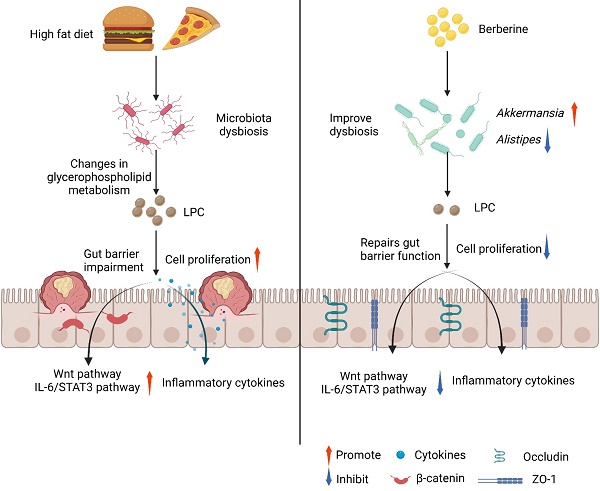
Dietary fat intake is positively associated with elevated risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). Currently, clinical treatments remian inadequate bacause of the complex pathogenesis of CRC induced by a high-fat diet (HFD). Mechanistically, imbalances in gut microbiota are associated with HFD-associated colorectal tumourigenesis. Therefore, we investigated the anti-tumor activity of berberine (BBR) in modulating the dysregulated gut microbiota and related metabolites by preforming 16S rDNA sequencing and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. As expected, BBR treatment significantly decreased the number of colonic polyps, ameliorated gut barrier disruption, and inhibited colon inflammation and related oncogenic pathways in AOM/DSS-induced CRC model mice fed with an HFD. Furthermore, BBR alleviated gut microbiota dysbiosis and increased the abundance of beneficial gut microorganisms, including Akkermansia and Parabacteroides, in HFD-fed CRC mice. In addition, metabolomics analysis demonstrated significantly altered the glycerophospholipid metabolism during the progression of HFD-associated CRC in mice, whereas BBR treatment reverted these changes in glycerophospholipid metabolites, particularly lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), which was confirmed to promote CRC cell proliferation and ameliorate cell junction impairment. Notably, BBR had no clear anti-tumor effects on HFD-fed CRC model mice with gut microbiota depletion, whereas transplantation of BBR-treated gut microbiota to gut microbiota-depleted CRC mice recapitulated the inhibitory effects of BBR on colorectal tumourigenesis and LPC levels. This study demonstrated that BBR inhibited HFD-associated CRC directly through modulating gut microbiota-regulated LPC levels, thereby providing a promising microbiota-modulating therapeutic strategy for the clinical prevention and treatment of Western diet-associated CRC.
Keywords: Berberine, Western diet, Colorectal cancer, Microbiome, Glycerophospholipid metabolism, Wnt pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact