10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(7):2150-2166. doi:10.7150/ijbs.80441 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Olfactomedin-4 deletion exacerbates DSS-induced colitis through a matrix metalloproteinase-9-dependent mechanism
Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China
* Contributed equally
Abstract
Background and Aims: Olfactomedin-4 is a glycoprotein that is upregulated in inflamed gastrointestinal tissues. This study aimed to investigate the role and underlying mechanisms of olfactomedin-4 in ulcerative colitis.
Methods: C57BL/6 mice and olfactomedin-4 knockout mice were fed dextran sulfate sodium in drinking water to establish a colitis model. An in vitro inflammation model was constructed in HCT116 and NCM460 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. The expression of olfactomedin-4 was detected by Western blotting, immunohistochemistry staining, and qRT‒PCR. The differences in the severity of colitis between olfactomedin-4 knockout mice and wild-type mice were compared, and the underlying mechanisms were explored.
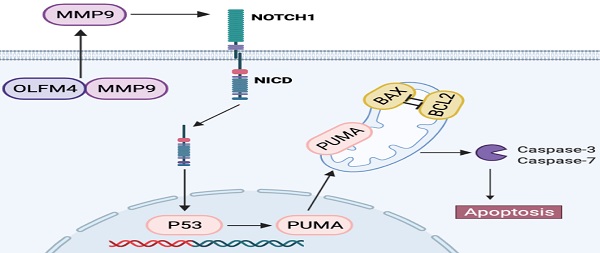
Results: Olfactomedin-4 expression was significantly upregulated in colonic tissues of active ulcerative colitis patients and in cellular and mouse models of colitis. Compared with wild-type littermates, olfactomedin-4 knockout mice were more susceptible to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and produced higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. In addition, olfactomedin-4 deficiency significantly promoted intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and increased intestinal permeability, which was mediated by the p53 pathway. Moreover, olfactomedin-4 directly interacted with and negatively regulated matrix metalloproteinase-9. Inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-9 significantly decreased colonic p53 expression and ameliorated experimental colitis in olfactomedin-4 knockout mice, while overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 aggravated colitis. Further experiments showed that matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulated p53 through the Notch1 signaling pathway to promote ulcerative colitis progression.
Conclusions: Olfactomedin-4 is significantly upregulated in ulcerative colitis and may protect against colitis by directly inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-9 and further decreasing p53-mediated apoptosis via Notch1 signaling.
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis, olfactomedin-4, matrix metalloproteinase-9, apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact