10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(7):2270-2288. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81415 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Drug Repurposing Flubendazole to Suppress Tumorigenicity via PCSK9-dependent Inhibition and Potentiate Lenvatinib Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Cancer Institute, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery Department I, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing 100142, China
4. Cancer Institute of Guangxi, Nanning 530015, China.
5. Qidong Liver Cancer Institute, Qidong 226299, China.
6. Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, China.
† These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
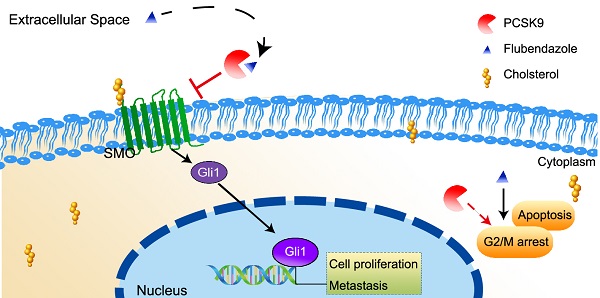
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal malignant cancers across the world. It has a poor prognosis and lacks effective therapies, especially for patients with advanced-stage cancer, indicating an urgent need for new therapies and novel therapeutic targets. Here, by screening the U.S. Food and Drug Administration drug library against HCC cell lines, we identified that flubendazole, a traditional anthelmintic drug, could prominently suppress HCC cells in vivo and in vitro. RNA sequence analysis and cellular thermal shift assays showed that flubendazole reduced the expression of PCSK9 protein by direct targeting. The increased expression of PCSK9 in HCC tissues was demonstrated to be correlated with poor prognosis, and the inhibitory ability of flubendazole was selectively dependent on PCSK9 expression. PCSK9 knockdown abolished the antitumor effects of flubendazole in HCC. Mechanistically, flubendazole inhibited the Hedgehog signaling pathway induced by PCSK9, resulting in the downregulation of smoothened (SMO) and GLI Family Zinc Finger 1 (Gli1). Moreover, combining flubendazole with lenvatinib was found more effective than administering lenvatinib only for HCC treatment in vivo and in vitro. These findings reveal the therapeutic potential of flubendazole against HCC and provide clues on new repurposed drugs and targets for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Drug repurposing, Flubendazole, Hepatocellular carcinoma, PCSK9

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact