10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(8):2366-2381. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79163 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of JNK/c-Jun-ATF2 Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance in Liver Cancer through down-Regulating Galectin-1
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province 519000, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Engineering Research Center of Molecular Imaging, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province 519000, China
3. Center for Interventional Medicine, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province 519000, China
4. Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province 510080, China
* Fan Yang, Mengzhu Li, Duo Xu and Zebo Jiang are co-first authors.
Abstract
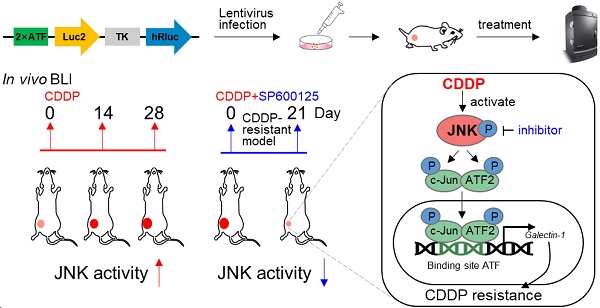
Due to drug resistance, the clinical response to cisplatin (CDDP) from patients with liver cancer is unsatisfactory. The alleviation or overcoming of CDDP resistance is an urgent problem to be solved in clinics. Tumor cells rapidly change signal pathways to mediate drug resistance under drug exposure. Here, multiple phosphor-kinase assays were performed and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) was activated in liver cancer cells treated with CDDP. The high activity of the JNK promotes poor progression and mediates cisplatin resistance in liver cancer, leading to a poor prognosis of liver cancer. Mechanistically, the highly activated JNK phosphorylated c-Jun and ATF2 formed a heterodimer to upregulate the expression of Galectin-1, leading to promoting cisplatin resistance in liver cancer. Importantly, we simulated the clinical evolution of drug resistance in liver cancer by continuous CDDP administration in vivo. In vivo bioluminescence imaging showed the activity of JNK gradually increased during this process. Moreover, the inhibition of JNK activity by small molecular or genetic inhibitors enhanced DNA damage and overcame CDDP resistance in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, our results underline that the high activity of JNK/c-Jun-ATF2/Galectin-1 mediates cisplatin resistance in liver cancer and provides an optional scheme for dynamic monitoring of molecular activity in vivo.
Keywords: In vivo bioluminescence imaging, Cisplatin, Resistance, JNK, Liver cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact