10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(8):2495-2514. doi:10.7150/ijbs.74315 This issue Cite
Review
Dysregulated MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Comprehensive Review
1. Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Nephrology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
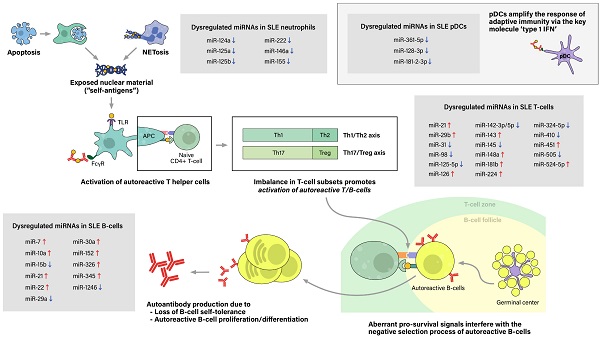
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease of which clinical presentation is vastly heterogeneous, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe renal diseases. Treatment goal of this illness is to minimize disease activity and prevent further organ damage. In recent years, much research has been done on the epigenetic aspects of SLE pathogenesis, for among the various factors known to contribute to the pathogenic process, epigenetic factors, especially microRNAs, bear the most therapeutic potential that can be altered unlike congenital genetic factors. This article reviews and updates what has been discovered so far about the pathogenesis of lupus, while focusing on the dysregulation of microRNAs in lupus patients in comparison to healthy controls along with the potentially pathogenic roles of the microRNAs commonly reported to be either upregulated or downregulated. Furthermore, this review includes microRNAs of which results are controversial, suggesting possible explanations for such discrepancies and directions for future research. Moreover, we aimed to emphasize the point that had been overlooked so far in studies regarding microRNA expression levels; that is, which specimen was used to assess the dysregulation of microRNAs. To our surprise, a vast number of studies have not considered this factor and have analyzed the potential role of microRNAs in general. Despite extensive investigations done on microRNA levels, their significance and potential role remain a mystery, which calls for further studies on this particular subject in regard of which specimen is used for assessment.
Keywords: microRNA (miRNA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), T lymphocyte, B lymphocyte, plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC)

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact