10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(8):2572-2587. doi:10.7150/ijbs.83530 This issue Cite
Research Paper
C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 inhibition reduces liver fibrosis by restoring the immune cell landscape
1. Lab of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology; West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
3. Department of Gastroenterology; General Hospital of Tibet Military Command, Lhasa, China.
#Yangkun Guo, Chong Zhao, and Wenting Dai contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
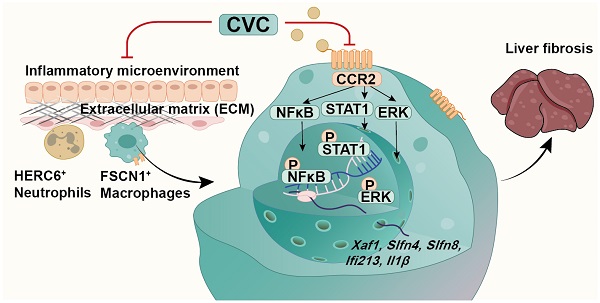
The accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in the liver leads to liver fibrosis and end-stage liver cirrhosis. C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) is an attractive target for treating liver fibrosis. However, limited investigations have been conducted to explore the mechanism by which CCR2 inhibition reduces ECM accumulation and liver fibrosis, which is the focus of this study. Liver injury and liver fibrosis were induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in wild-type mice and Ccr2 knockout (Ccr2-/-) mice. CCR2 was upregulated in murine and human fibrotic livers. Pharmacological CCR2 inhibition with cenicriviroc (CVC) reduced ECM accumulation and liver fibrosis in prevention and treatment administration. In single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), CVC was demonstrated to alleviate liver fibrosis by restoring the macrophage and neutrophil landscape. CVC administration and CCR2 deletion can also inhibit the hepatic accumulation of inflammatory FSCN1+ macrophages and HERC6+ neutrophils. Pathway analysis indicated that the STAT1, NFκB, and ERK signaling pathways might be involved in the antifibrotic effects of CVC. Consistently, Ccr2 knockout decreased phosphorylated STAT1, NFκB, and ERK in the liver. In vitro, CVC could transcriptionally suppress crucial profibrotic genes (Xaf1, Slfn4, Slfn8, Ifi213, and Il1β) in macrophages by inactivating the STAT1/NFκB/ERK signaling pathways. In conclusion, this study depicts a novel mechanism by which CVC alleviates ECM accumulation in liver fibrosis by restoring the immune cell landscape. CVC can inhibit profibrotic gene transcription via inactivating the CCR2-STAT1/NFκB/ERK signaling pathways.
Keywords: single-cell RNA sequencing, macrophage, neutrophil, STAT1, NFκB, ERK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact