10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2835-2847. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84060 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ability of Local Clearance of Senescent Cells in Ipsilateral Hemisphere to Mitigate Acute Ischemic Brain Injury in Mice
1. Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
2. Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
3. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
4. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
5. Department of Ecology & Environmental Sciences, School of Life Science, Pondicherry University, Kalapet, India.
6. School of Respiratory Therapy, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
*Lu and Sheu contribute equally.
Abstract
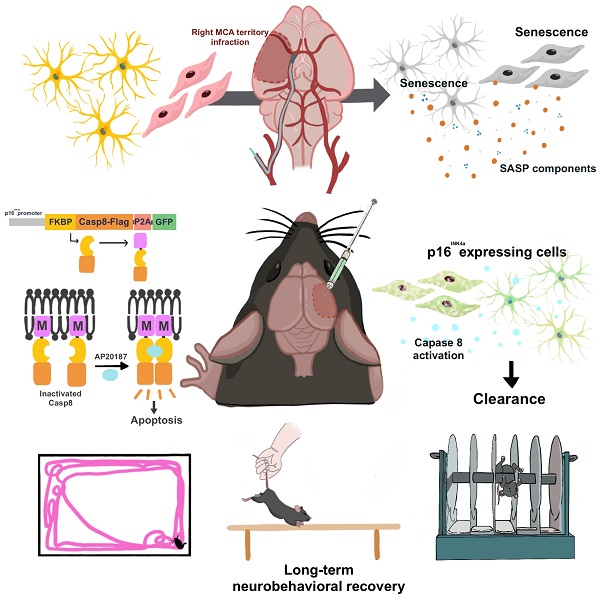
Senolytic treatment has potential therapeutic efficacy for acute ischemic stroke (AIS). However, the systemic treatment of senolytics may produce off-target side effects and a toxic profile, which affect analysis of the role of acute senescence of neuronal cells in pathogenesis of AIS. We constructed a novel lenti-INK-ATTAC viral vector to introduce INK-ATTAC genes to the ipsilateral brain and locally eliminate senescent brain cells by administering AP20187 to activate caspase-8 apoptotic cascade. In this study, we have found that acute senescence is triggered by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgery, particularly in astrocytes and cerebral endothelial cells (CECs). The upregulation of p16INK4a and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors including matrix metalloproteinase-3, interleukin-1 alpha and -6 were observed in oxygen-glucose deprivation-treated astrocytes and CECs. The systemic administration of a senolytic, ABT-263, prevented the impairment of brain activity from hypoxic brain injury in mice, and significantly improved the neurological severity score, rotarod performance, locomotor activity, and weight loss. The treatment of ABT-263 reduced senescence of astrocytes and CECs in MCAO mice. Furthermore, the localized removal of senescent cells in the injured brain through the stereotaxical injection of lenti-INK-ATTAC viruses generates neuroprotective effects, protecting against acute ischemic brain injury in mice. The content of SASP factors and mRNA level of p16INK4a in the brain tissue of MCAO mice were significantly reduced by the infection of lenti-INK-ATTAC viruses. These results indicate that local clearance of senescent brain cells is a potential therapy on AIS, and demonstrate the correlation between neuronal senescence and pathogenesis of AIS.
Keywords: senolytic treatment, acute ischemic stroke, lenti-INK-ATTAC viral vector

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact