10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(10):3249-3265. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81900 This issue Cite
Research Paper
β-amyloid binds to microglia Dectin-1 to induce inflammatory response in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
1. Affiliated Yongkang First People's Hospital and School of Pharmacy, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310012, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines of the Changbai Mountain, Ministry of Education, College of Pharmacy, Yanbian University, Yanji, Jilin, 133002, China.
3. Chemical Biology Research Center, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang,325035, China.
4. Oujiang Laboratory (Zhejiang Lab for Regenerative Medicine, Vision and Brain Health); Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang,325035, China.
# Equal contribution
Abstract
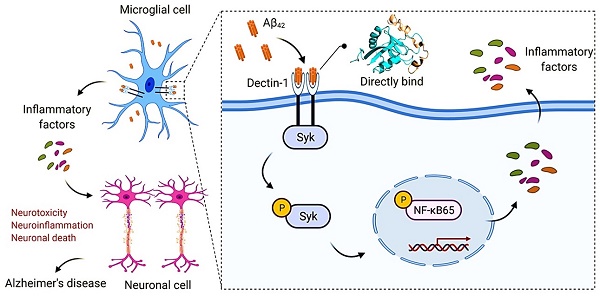
Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation is closely related to the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the early stages of the inflammation response, pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a key role in clearing damaged cells and defending against infection by recognizing endogenous and exogenous ligands. However, the regulation of pathogenic microglial activation and its role in AD pathology remains poorly understood. Here we showed that a pattern recognition receptor called Dectin-1, expressed on microglia, mediates the pro-inflammatory responses of beta-amyloid (Aβ). Knockout of Dectin-1 reduced Aβ1-42 (Aβ42)-induced microglial activation, inflammatory responses, and synaptic and cognitive deficits in Aβ42-infused AD mice. Similar results were obtained in the BV2 cell model. Mechanistically, we showed that Aβ42 could directly bind to Dectin-1, causing Dectin-1 homodimerization and activating downstream spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway to induce the expression of inflammatory factors and, in turn, AD pathology. These results suggest the important role of microglia Dectin-1 as a new direct receptor for Aβ42 in microglial activation and AD pathology and provide a potential therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation in AD.
Keywords: β-amyloid, Dectin-1, Microglia, Neuroinflammation, Alzheimer's disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact