10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(12):3726-3743. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85674 This issue Cite
Review
Broadening horizons: the multifaceted functions of ferroptosis in kidney diseases
1. Research Institute of Nephrology, Zhengzhou University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China
2. Traditional Chinese Medicine Integrated Department of Nephrology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China
3. Henan Province Research Center for Kidney Disease, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China
4. Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Chronic Kidney Disease in Henan Province, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China
5. Clinical Systems Biology Laboratories, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, 450052, P. R. China
6. Department of Pharmacy, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China.
7. Blood Purification Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, P. R. China.
#Qi Feng, Yang Yang, and Kaidi Ren made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
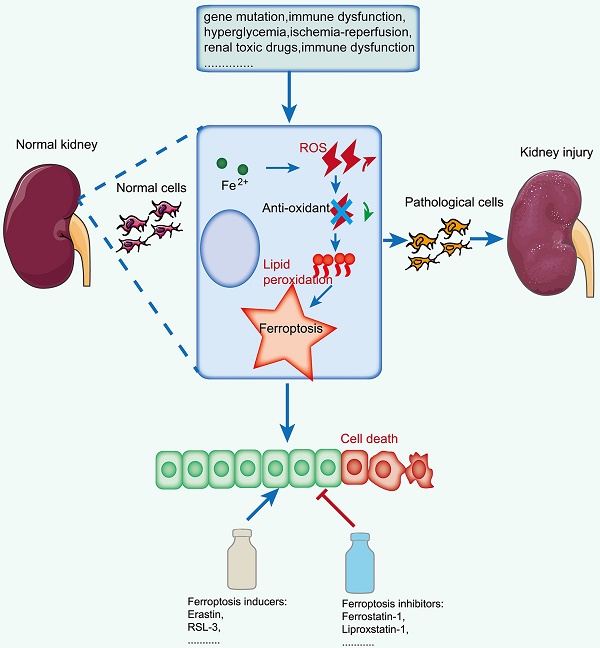
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent programmed cell death pattern that is characterized by iron overload, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and lipid peroxidation. Growing viewpoints support that the imbalance of iron homeostasis and the disturbance of lipid metabolism contribute to tissue or organ injury in various kidney diseases by triggering ferroptosis. At present, the key regulators and complicated network mechanisms associated with ferroptosis have been deeply studied; however, its role in the initiation and progression of kidney diseases has not been fully revealed. Herein, we aim to discuss the features, key regulators and complicated network mechanisms associated with ferroptosis, explore the emerging roles of organelles in ferroptosis, gather its pharmacological progress, and systematically summarize the most recent discoveries about the crosstalk between ferroptosis and kidney diseases, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC), acute kidney injury (AKI), diabetic kidney disease (DKD), autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), renal fibrosis, lupus nephritis (LN) and IgA nephropathy. We further conclude the potential therapeutic strategies by targeting ferroptosis for the prevention and treatment of kidney diseases and hope that this work will provide insight for the further study of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of kidney-related diseases.
Keywords: ferroptosis, kidney diseases, molecular mechanism, pharmacological progress

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact