10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):414-432. doi:10.7150/ijbs.89368 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Elevated SLC40A1 impairs cardiac function and exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in ischemic myocardia
1. Department of Cardiology, Tangdu Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, 710032, China.
2. Department of Orthodontics, Stomatology Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, 710032, China.
3. Department of Cardiology, NO. 988 Hospital of Joint Logistic Sopport Force, Zhengzhou, 450007, China.
# These authors contributed equally at the paper.
Abstract
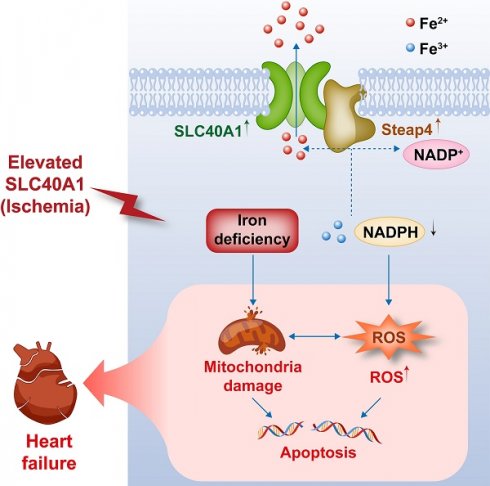
Iron homeostasis is crucial for optimal cardiac function. Iron deficiency and overload have been linked to the development of cardiomyopathy and heart failure (HF) via intricate mechanisms. Although the crucial role of SLC40A1 in iron metabolism by facilitating the efflux of cellular iron has been confirmed, its specific molecular functions in cardiovascular diseases remain poorly understood. In this study, we generated mice with inducible cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of SLC40A1 for the first time. The overexpression of SLC40A1 in the cardiomyocytes of adult mice resulted in significant iron deficiency, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, subsequently resulting in the development of fatal HF. Notably, SLC40A1 upregulation was observed in the ischemic region during the initial phase of myocardial infarction (MI), contributing to iron loss in the cardiomyocytes. Conversely, the cardiomyocyte-specific knockdown of SLC40A1 improved cardiac dysfunction after MI by enhancing mitochondrial function, suppressing oxidative stress, and reducing cardiomyocytes apoptosis. Mechanistically, Steap4 interacted with SLC40A1, facilitating SLC40A1-mediated iron efflux from cardiomyocytes. In short, our study presents evidence for the involvement of SLC40A1 in the regulation of myocardial iron levels and the therapeutic benefits of cardiomyocyte-specific knockdown of SLC40A1 in MI in mice.
Keywords: Iron, SLC40A1, Steap4, Heart failure, Myocardial infarction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact