10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):446-463. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86085 This issue Cite
Research Paper
VEGFA/NRP-1/GAPVD1 axis promotes progression and cancer stemness of triple-negative breast cancer by enhancing tumor cell-macrophage crosstalk
1. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710061, China.
2. Department of Respiratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710061, China.
3. Department of Pathology, Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710068, China.
4. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710004, China.
5. Department of Forensic Medicine, Medical School of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710061, China.
6. Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, 710061, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
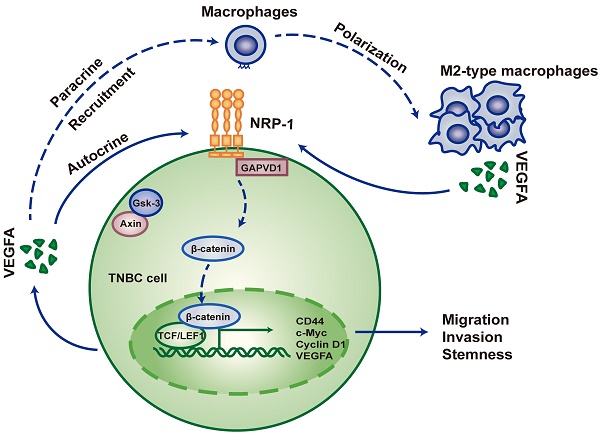
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has long been considered a major clinical challenge due to its aggressive behavior and poor prognosis. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are known as the main cells responsible for tumor origination, progression, recurrence and metastasis. Here, we report that M2-type tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) contribute to cancer stemness in TNBC cells via the secretion of VEGFA. Reciprocally, elevated VEGFA expression by TAM-educated TNBC cells acts as a regulator of macrophage polarization, therefore constitute a feed-back loop between TNBC cells and TAMs. Mechanistically, VEGFA facilitates the CSC phenotype via the NRP-1 receptor and downstream GAPVD1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in TNBC cells. Our study underscores the crosstalk between TNBC cells and TAMs mediated by VEGFA and further clarifies the role and underlying mechanisms of the VEGFA/NRP-1/GAPVD1 axis in regulating cancer stemness. We also document an immunosuppressive function of VEGFA in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Therefore, the present study indicates crosstalk between TNBC cells and TAMs induced by VEGFA and provides a potential implication for the combination of immunotherapy and VEGFA-targeted agents in TNBC therapy.
Keywords: Triple-negative breast cancer, cancer stem cell, VEGFA/NRP-1/GAPVD1 axis, tumor-associated macrophage.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact