10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(2):156-171. doi:10.7150/ijbs.13537 This issue Cite
Review
Recent Developments in Using Advanced Sequencing Technologies for the Genomic Studies of Lignin and Cellulose Degrading Microorganisms
Department of Biology, Lakehead University, 955 Oliver Road, Thunder Bay, Ontario, P7B 5E1, Canada.
Abstract
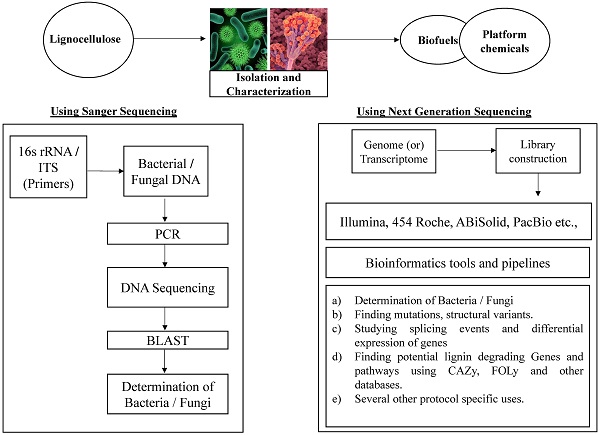
Lignin is a complex polyphenyl aromatic compound which exists in tight associations with cellulose and hemicellulose to form plant primary and secondary cell wall. Lignocellulose is an abundant renewable biomaterial present on the earth. It has gained much attention in the scientific community in recent years because of its potential applications in bio-based industries. Microbial degradation of lignocellulose polymers was well studied in wood decaying fungi. Based on the plant materials they degrade these fungi were classified as white rot, brown rot and soft rot. However, some groups of bacteria belonging to the actinomycetes, α-proteobacteria and β-proteobacteria were also found to be efficient in degrading lignocellulosic biomass but not well understood unlike the fungi. In this review we focus on recent advancements deployed for finding and understanding the lignocellulose degradation by microorganisms. Conventional molecular methods like sequencing 16s rRNA and Inter Transcribed Spacer (ITS) regions were used for identification and classification of microbes. Recent progression in genomics mainly next generation sequencing technologies made the whole genome sequencing of microbes possible in a great ease. The whole genome sequence studies reveals high quality information about genes and canonical pathways involved in the lignin and other cell wall components degradation.
Keywords: Lignocellulose, Fungi, Bacteria, 16s rRNA, Inter Transcribed Spacer, Biodegradation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact