10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(12):1540-1546. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23000 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Specific Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2-Expressing Cells Leads to Defects in Epiphyseal Bone
1. Department of Pharmacy, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China
2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL 60612, USA
3. Department of Medical Cell Biology and Genetics, Shenzhen Key Laboratory and the Center for Anti-Ageing and Regenerative Medicine, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
4. Department of Biologic and Materials Science, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
5. Zhejiang Cancer Research Institute, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310022, China
6. Collaborative Innovation Center of Tianjin Metabolic Diseases Hospital, Key Laboratory of Hormones and Development (Ministry of Health), Metabolic Diseases Hospital & Institute of Endocrinology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
Abstract
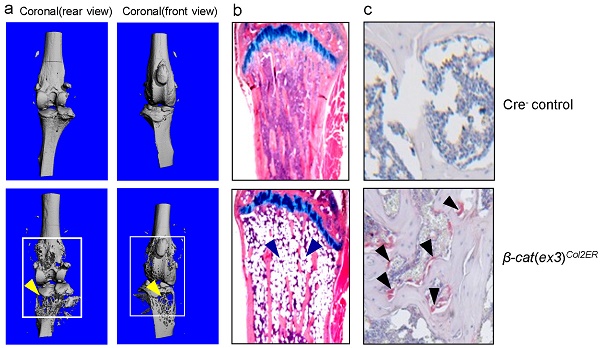
The role of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in postnatal bone growth has not been fully defined. In the present studies, we generated β-catenin conditional knockout (KO) mice and deleted β-catenin in Col2-expressing chondrocytes and mesenchymal progenitor cells. Findings from analyzing the β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice revealed severe bone destruction and bone loss phenotype in epiphyseal bone, probably due to the increase in osteoclast formation and the accumulation of adipocytes in this area. In addition, we also found bone destruction and bone loss phenotype in vertebral bone in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. These findings indicate that β-catenin signaling plays a critical role in postnatal bone remodeling. Our study provides new insights into the regulation of epiphyseal bone homeostasis at postnatal stage.
Keywords: Epiphysis, Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Postnatal Bone Growth, Osteoarthritis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact