10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(4):788-799. doi:10.7150/ijbs.30677 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Farrerol Ameliorates APAP-induced Hepatotoxicity via Activation of Nrf2 and Autophagy
Institute of Translational Medicine, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130001, China
Abstract
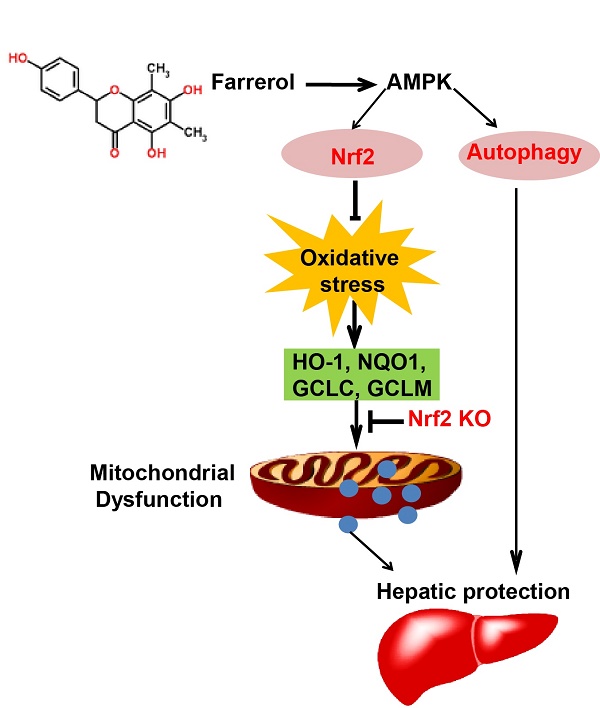
Farrerol has been shown to have antioxidative potential via Nrf2 activation, which in turn is involved in the prevention of hepatotoxicity. The purpose of the current study was to explore the protective effect of farrerol against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity and its underlying mechanisms. Mice were used to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of farrerol on liver injury induced by acetaminophen in vivo. HepG2 cells were utilized to further determine the functional role and mechanisms by which Nrf2 and autophagy are involved in the hepatoprotective effect of farrerol in vitro. We found that treatment with farrerol leads to a significant reduction in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by decreasing mortality, histopathological liver changes, and ALT and AST levels. Furthermore, farrerol effectively suppressed mitochondrial dysfunction by reducing JNK phosphorylation, Bax mitochondrial translocation, AIF and cytochrome c release. Further investigations revealed that the activation of Nrf2 and the induction of autophagy via the AMPK/AKT pathway by farrerol contributed to its hepatoprotective activity in vitro. In addition, farrerol inhibited acetaminophen-induced the mortality and histopathological changes in WT mice were evidently alleviated but not abrogated in Nrf2 -/- mice, which attributed to the induction of autophagy. Together, farrerol has protective potential against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity which may be associated with activation of Nrf2 and autophagy.
Keywords: Farrerol, APAP, Hepatotoxicity, Nrf2, Autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact