10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(2):635-650. doi:10.7150/ijbs.52319 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ITGB1 enhances the Radioresistance of human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by modulating the DNA damage response and YAP1-induced Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition
1. Department of Oncology, Shengjing Hospital affiliated with China Medical University, Shenyang 110004, China.
2. School and Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases.
Abstract
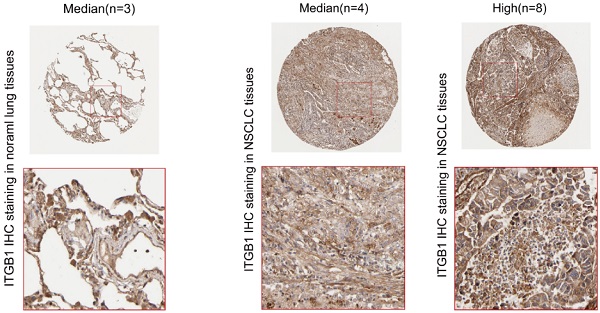
Objectives: Radiotherapy has played a limited role in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) due to the risk of tumour radioresistance. We previously established the radioresistant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line H460R. In this study, we identified differentially expressed genes between these radioresistant H460R cells and their radiosensitive parent line. We further evaluated the role of a differentially expressed gene, ITGB1, in NSCLC cell radioresistance and as a potential target for improving radiosensitivity.
Materials and Methods: The radiosensitivity of NSCLC cells was evaluated by flow cytometry, colony formation assays, immunofluorescence, and Western blotting. Bioinformatics assay was used to identify the effect of ITGB1 and YAP1 expression in NSCLC tissues.
Results: ITGB1 mRNA and protein expression levels were higher in H460R than in the parental H460 cells. We observed lower clonogenic survival and cell viability and a higher rate of apoptosis of ITGB1-knockdown A549 and H460R cells than of wild type cells post-irradiation. Transfection with an ITGB1 short hairpin (sh) RNA enhanced radiation-induced DNA damage and G2/M phase arrest. Moreover, ITGB1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of NSCLC cells. Silencing ITGB1 suppressed the expression and intracellular translocation of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), a downstream effector of ITGB1.
Conclusions: ITGB1 may induce radioresistance via affecting DNA repair and YAP1-induced EMT. Taken together, our data suggest that ITGB1 is an attractive therapeutic target to overcome NSCLC cell radioresistance.
Keywords: ITGB1, Yes-associated protein (YAP), radioresistance, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact