10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(4):972-985. doi:10.7150/ijbs.55887 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Circulating Exosomal miR-1-3p from Rats with Myocardial Infarction Plays a Protective Effect on Contrast-Induced Nephropathy via Targeting ATG13 and activating the AKT Signaling Pathway
1. Section of Pacing and Electrophysiology, Division of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
2. Department of Cardiology, the Affiliated Changzhou No. 2 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou, China.
* The authors contributed equally to this study
Abstract
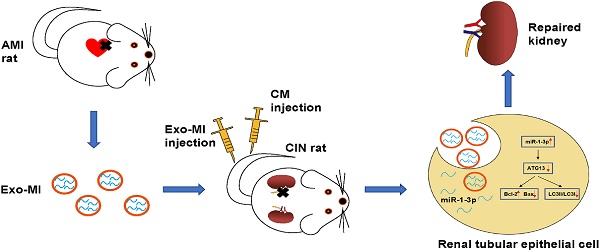
Rationale: With the widespread development of the interventional technique for cardiovascular diseases and the widespread use of contrast medium (CM), the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) has been increasing, which is associated with poor prognosis for cardiovascular diseases. This study aims to explore the effect of circulating exosomal microRNA from patients with myocardial infarction (MI) on CIN and related molecular mechanism. Methods: A rat MI model was established by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery. Circulating exosomes were isolated from control (Exo-NC) and MI rats (Exo-MI) using a commercial kit. The in vivo and in vitro models of CIN were created using iodixanol. Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was utilized to detect the expression of miR-1-3p. Western blot (WB) was used to detect the expression of exosomal surface markers, and apoptosis-related and autophagy-related proteins. The apoptosis rate was examined by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining and flow cytometry (FC). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was utilized to observe the exosomes and autophagosomes. Rat kidney injury was assessed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) immunohistochemical staining. Renal function of rats was assessed by detecting the levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (Cr). The dual luciferase reporter assay was performed to identify the target gene of miR-1-3p. Results: The treatment of CM induced NRK-52E cell damage, which manifested as enhanced cell autophagy and enhanced apoptosis. The Exo-MI treatment significantly inhibited the CM-induced autophagy and apoptosis of NRK-52E cells. Furthermore, the Exo-MI treatment increased the Bcl-2 expression, but decreased the Bax expression and the ratio of LC3II/LC3I. Furthermore, the results of the TUNEL staining and FC showed that Exo-MI can reduce apoptotic rate. Through TEM, it was found that Exo-MI reduced the number of autophagosomes in NRK-52E cells. The rescue experiments revealed that the function of Exo-MI is to inhibit the CM-induced autophagy and apoptosis of NRK-52E cells, which can be inhibited by the miR-1-3p inhibitor. Furthermore, it was found that the overexpression of miR-1-3p can also inhibit the CM-induced autophagy and apoptosis of NRK-52E cells. Through dual luciferase reporter assay, ATG13 was found to be the target of miR-1-3p. In addition, the overexpression of miR-1-3p significantly reversed the CM-induced decrease in phosphorylation level of AKT. Furthermore, ATG13 silencing can also inhibit the CM-induced autophagy and apoptosis of NRK-52E cells. In vivo, Exo-MI significantly alleviated the renal injury, reduced the renal fibrosis, and improved the renal function of CIN rats. Conclusion: The circulating exosomal miR-1-3p after MI inhibited the CM-induced apoptosis and autophagy of renal tubular epithelial cells, and improved the renal function of rats by targeting ATG13 and activating the AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: Contrast-induced nephropathy, Contrast medium, Iodixanol, Exosome, MiR-1-3p, ATG13, AKT signaling pathway.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact