Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(2):571-592. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70211 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sesn2 Serves as a Regulator between Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Mitophagy in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
1. Department of Spinal Surgery, Orthopedic Medical Center, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, China.
2. Department of Clinic of Spine Center, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200082, China.
3. Department of Orthopedics, Orthopedic Research Institute, West China Hospital, Sichuan University.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
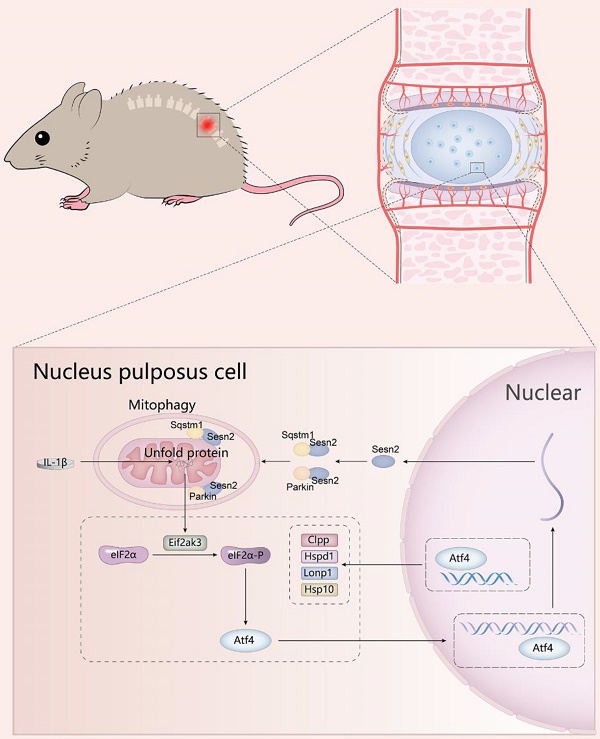
Mitochondrial unfold protein response (UPRmt) can induce mitophagy to protect cell from unfold protein. However, how UPRmt induces mitophagy to protect cell is not yet clear. Herein, Sesn2 was considered to be a key molecule that communicated UPRmt and mitophagy in the intervertebral disc. Silencing of Sesn2 was able to reverse the protective effects of Nicotinamide riboside (NR) on nucleus pulposus (NP) cells and inhibit mitophagy induced by UPRmt. UPRmt upregulated Sesn2 through Eif2ak4/eIF2α/Atf4, and further induced mitophagy. Sesn2 promoted the translocation of cytosolic Parkin and Sqstm1 to the defective mitochondria respectively, thereby enhancing mitophagy. The translocation of cytosolic Sqstm1 to the defective mitochondria was dependent on Parkin. The two functional domains of Sesn2 were necessary for the interaction of Sesn2 with Parkin and Sqstm1. The cytosolic interaction of Sesn2 between Parkin and Sqstm1 was independent on Pink1 (named as PINK1 in human) but the mitochondrial translocation was dependent on Pink1. Sesn2-/- mice showed a more severe degeneration and NR did not completely alleviate the intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) of Sesn2-/- mice. In conclusion, UPRmt could attenuate IVDD by upregulation of Sesn2-induced mitophagy. This study will help to further reveal the mechanism of Sesn2 regulating mitophagy, and open up new ideas for the prevention and treatment of IVDD.
Keywords: Intervertebral disc degeneration, Mitochondrial unfold protein response, Sesn2, Mitophagy.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact