10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(13):4166-4180. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86855 This issue Cite
Review
Molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis and its role in anti-tumor immunity
1. The First Clinical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, 524023, Guangdong, China.
2. Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518036, China; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Inflammatory and Immunology Diseases, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518036, China.
3. The Marine Biomedical Research Institute, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, 524023, Guangdong, China.
4. The Marine Biomedical Research Institute of Guangdong Zhanjiang, Zhanjiang, 524023, Guangdong, China.
# Equal contribution.
Abstract
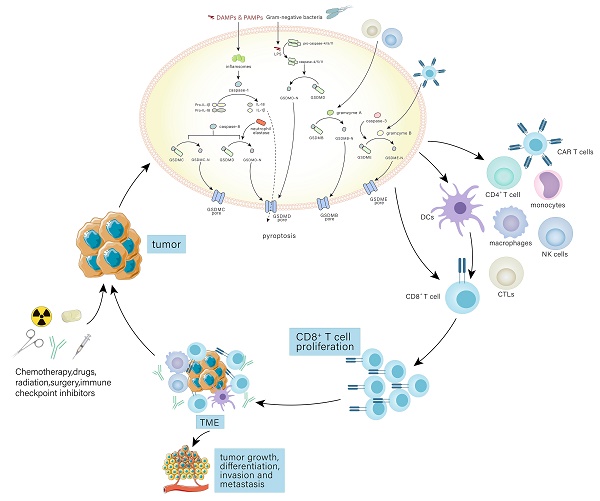
Pyroptosis is a form of cell death that is characterized by the destruction of the cell, and it has implications in both the immune system and cancer immunotherapy. The gasdermin family is responsible for the activation of pyroptosis, which involves the formation of pores in the cellular membrane that permit the discharge of inflammatory factors. The inflammasome response is a powerful mechanism that helps to eliminate bacteria and cancer cells when cellular damage occurs. As tumor cells become more resilient to apoptosis, other treatments for cancer are becoming more popular. It is essential to gain a thorough understanding of pyroptosis in order to use it in cancer treatment, considering the intricate association between pyroptosis and the immune system's defensive reaction against tumors. This review offers an overview of the mechanisms of pyroptosis, the relationship between the gasdermin family and pyroptosis, and the interplay between pyroptosis and anti-tumor immunity. In addition, the potential implications of pyroptosis in cancer immunotherapy are discussed. Additionally, we explore future research possibilities and introduce a novel approach to tumor treatment.
Keywords: pyroptosis, tumor microenvironment, Gasdermin, inflammasome, antitumor immunity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact