10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(10):1234-1241. doi:10.7150/ijbs.21149 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Transarterial Chemoembolization: A Favorable Postoperative Management to Improve Prognosis of Hepatitis B Virus-associated Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma after Surgical Resection
1. Department of Liver Surgery, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200127, China.
2. International Cooperation Laboratory on Signal Transduction, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200438, China.
3. National Center for Liver Cancer, Shanghai 201805, China.
4. Department of Biliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China.
5. Department of Interventional Oncology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
*These authors equally contributed to the work.
Abstract
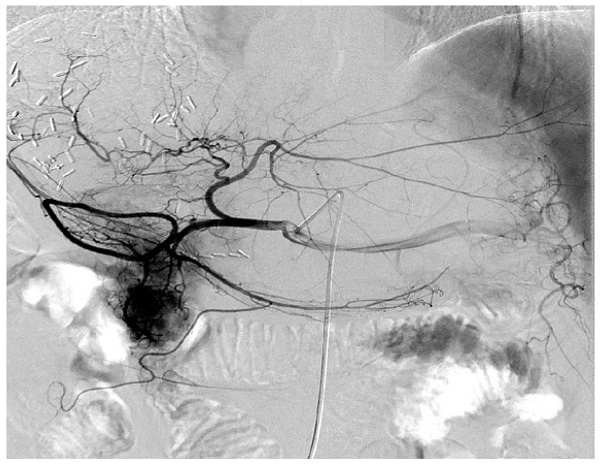
Background: There is no information regarding transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a postoperative management after hepatic resection for patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC).
Methods: Forty-two patients with pathological confirmation of HBV-associated ICC were enrolled. Prognostic impact of the clinicopathological factors as well as postoperative TACE were evaluated. Computed tomography findings of HBV-associated ICC were assessed.
Results: Tumor size of larger than 5 cm (hazard ratio [HR], 5.654; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.175 to 27.204; P = 0.031), postoperative TACE (HR, 0.123; 95% CI, 0.023 to 0.643; P = 0.013), and lymph node metastasis (HR, 3.284; 95% CI, 1.236 to 8.724; P = 0.017) revealed to be independently associated with survival outcomes of patients with HBV-associated ICC. Application of TACE, as a postoperative management to control early local recurrence on the basis of hepatic arterial phase enhancement, significantly prolonged survival outcomes (1-yr, 88.9%; 3-yr, 77.8%; 5-yr, 66.7%), compared to the patients who did not receive TACE (1-yr, 63.6%; 3-yr, 30.8%; 5-yr, 13.0%). When analyzed according to the status of hepatic arterial phase, arterial phase enhancement demonstrated a favorable trend on prognosis of patients with HBV-associated ICC without statistical significance (HR, 0.435; 95% CI, 0.140 to 1.359; P = 0.141), and TACE independently improved overall survival of patients with arterial phase enhancement (HR, 0.105; 95% CI, 0.014 to 0.774; P = 0.027).
Conclusions: Put together, our results indicate that postoperative TACE effectively improves prognosis of HBV-associated ICC with arterial phase enhancement in CT scans. Large-sized trials are required for our results to be applied in clinical medicine.
Keywords: transarterial chemoembolization, hepatitis B virus-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatic resection, computed tomography, arterial enhancement phase

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact