10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(12):1520-1531. doi:10.7150/ijbs.21107 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide prevents the disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress following spinal cord injury
1. Department of Orthopaedics, Taizhou Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Linhai, Zhejiang, 317000 PR China;
2. Key Laboratory of Orthopaedics of Zhejiang Province, Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035 PR China;
3. Molecular Pharmacology Research Center, School of Pharmacy, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035 PR China;
4. Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Cixi People's Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315300, PR China;
5. Department of Gastroenterology, Ningbo Medical Treatment Center Li Hui-li Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315040, PR China.
* These authors had equal contribution and are designated as co-first authors.
Abstract
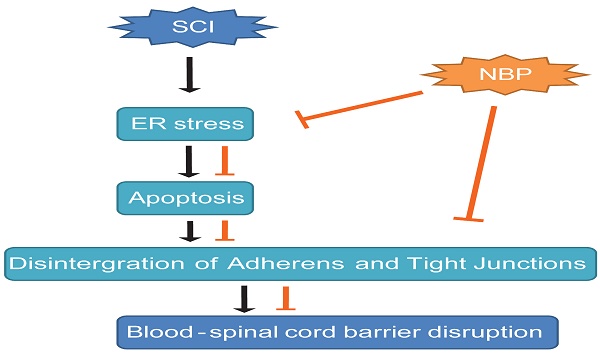
After spinal cord injury (SCI), the destruction of blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) is shown to accelerate gathering of noxious blood-derived components in the nervous system, leading to secondary neurodegenerative damages. SCI activates endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress), which is considered to evoke secondary damages of neurons and glia. Recent evidence indicates that Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) has the neuroprotective effect in ischaemic brain injury, but whether it has protective effects on SCI or not is largely unclear. Here, we show that NBP prevented BSCB disruption after SCI via inhibition of ER stress. Following a moderate contusion injury of the T9 level of spinal cord, NBP was administered by oral gavage and further treated once a day. NBP significantly attenuated BSCB permeability and breakdown of adherens junction (AJ) and tight junction (TJ) proteins, then improved locomotion recovery following SCI. The protective role of NBP on BSCB disruption is associated with the restrain of ER stress caused by SCI. Furthermore, NBP considerably constrained the expression of ER stress-associated proteins and degradation of TJ and AJ in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) treated with TG. In conclusion, our results indicate that ER stress is associated with the disruption of BSCB integrity after injury, NBP attenuates BSCB disruption via inhibiting ER stress and improve functional recovery following SCI.
Keywords: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide, Blood-spinal cord barrier, Spinal cord injury, Endocytoplasmic reticulum stress.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact