Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(1):81-92. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28304 This issue Cite
Research Paper
G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy via the Regulation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signalling and Autophagy
1. Department of Cardiology, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated with Shandong University, Shandong, China
2. Department of Cardiology, Shandong Provincial Chest Hospital, Shandong, China
3. Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Shandong, China
4. Taian Central Hospital, Taian City, Shandong, China
* H.P. and W.W. contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
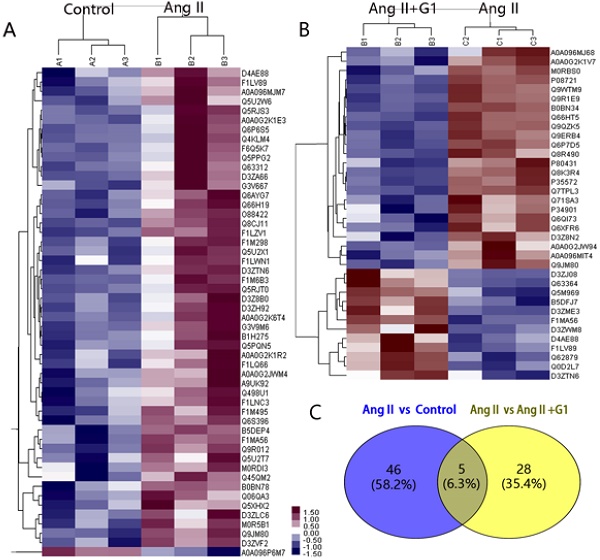
Estrogen has been demonstrated to protect the heart against cardiac remodelling and heart failure in women. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1) is a recently discovered estrogen receptor (ER) that is expressed in various tissues. However, the mechanisms by which estrogen protects the heart, especially the roles played by ERs, are not clear. In this study, we explored the effect of GPER1 activation on angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and the involved signalling pathways and mechanisms. Our data demonstrated that GPER1 is expressed in cardiomyocytes, a GPER1 agonist, G1, attenuated Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and downregulated the mRNA expression levels of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). Bioinformatics analysis revealed that five proteins, including RAP1gap, might be the key proteins involved in the attenuation of Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by GPER1. G1 increased the protein level of p-Akt, p-70S6K1 and p-mTOR but decreased p-4EBP1 expression. All these effects were inhibited by either G15 (a GPER1 antagonist) or MK2206 (an inhibitor of Akt). Autophagy analysis showed that the LC3II/LC3I ratio was increased in Ang II-treated cells, and the increase was inhibited by G1 treatment. The effect of G1 on autophagy was blocked by treatment with G15, rapamycin, and MK2206. These results suggest that GPER1 activation attenuates Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by upregulating the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signalling pathway and inhibiting autophagy.
Keywords: Angiotensin II (Ang II), cardiac hypertrophy, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1), Akt, autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact