Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(16):3200-3209. doi:10.7150/ijbs.51293 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel miR-7156-3p-HOXD13 axis modulates glioma progression by regulating tumor cell stemness
1. Department of Radiology, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400042, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burn and Combined Injury, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400042, China.
3. Chongqing Clinical Research Center of Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Chongqing 400042, China.
4. Department of Neurosurgery, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400042, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
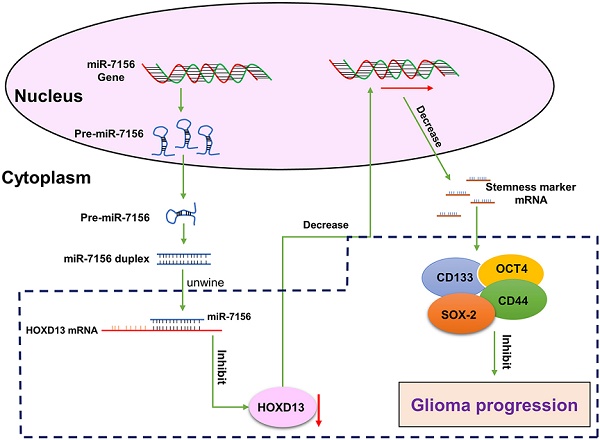
Malignant glioma is the most common brain tumor in adults. Despite the great advances in anti-glioma treatments which have led to significant improvement in clinical outcomes, tumor recurrence remains the major cause of mortality. Increased cancer cell stemness and invasiveness are correlated with glioma progression. By searching the Cancer Genome Atlas, we showed that the expression of miR-7156-3p is significantly decreased in glioma tissues compared to the normal brain, and the decreased level of miR-7156-3p is closely correlated with glioma grade and patient survival. Clinical study consistently confirmed that miR-7156-3p is negatively correlated with glioma grade. Cell culture and animal experiments revealed that inhibition of miR-7156-3p effectively stimulates glioma cell stemness, invasion, and growth. In contrast, the augmentation of miR-7156-3p inhibits these phenotypes. Using Next-generation sequencing combined with target prediction approach, Homeobox D13 (HOXD13) is identified as the target gene of miR-7156-3p and further validated by luciferase reporter assay and cell transfection experiments. Additional in vitro and animal experiments demonstrated that miR-7156-3p regulates glioma cell stemness, invasion, and growth by mediating HOXD13. In conclusion, our findings provide new insight into the regulation of glioma stemness and invasiveness and may propose a potential strategy for anti-glioma treatment. Moreover, miR-7156-3p may serve as a candidate biomarker for predicting glioma progression in clinical practice.
Keywords: miR-7156-3p, HOXD13, stemness, glioma, invasion, biomarker

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact