10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(16):3221-3230. doi:10.7150/ijbs.49410 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Upregulated GRB7 promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis of Bladder Cancer via Phospho-AKT Pathway
1. Department of Pathogen Biology and Immunology, School of Life Sciences and Biopharmaceutics, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
2. Shenzhen Long-gang Maternal and Child Health Hospital Centralab, Shenzhen 518172, China.
3. Department of Basic Medicine, Nanyang Medical College, Nanyang, Henan 473061, China.
4. Department of Physiology, School of Life Sciences and Biopharmaceutics, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
5. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Bioactive Substances, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
6. KingMed School of Laboratory Medicine, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510182, China.
7. Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
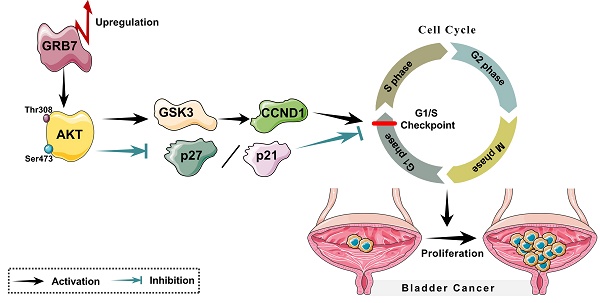
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 7 (GRB7) has been found closely related to the occurrence and development of various tumors, but its function in bladder cancer has not yet been elucidated. The study is aiming at investigating the expression and function of GRB7 in bladder cancer. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database was selected to analyze mRNA levels of GRB7 in bladder cancer. RT-qPCR and Western blot were conducted to detect the expression of GRB7 in normal bladder epithelial cells, seven bladder cancer cell lines and eight pairs of malignant/nonmalignant bladder tissues. The role of GRB7 in tumor proliferation and tumorigenesis was explored by establishing stable cells, in vitro cell experiments and in vivo xenograft models. The molecular regulation mechanism of GRB7 in bladder cancer was investigated by treatment with AKT inhibitor. GRB7 mRNA was upregulated in bladder cancer samples compared with that in normal tissue samples. Overexpressing GRB7 significantly promoted the proliferation and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. However, silencing GRB7 played the retarding part. GRB7 promoted G1/S transition by activating the AKT pathway. Our results indicate that GRB7 plays an important role in promoting proliferation and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer.
Keywords: GRB7, proliferation, bladder cancer, AKT, G1/S

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact