10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(15):4254-4270. doi:10.7150/ijbs.60805 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting BRAM1 to regulate SMAD and MAPK signaling pathways
1. Department of Physiology , Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117456, Singapore.
2. NUS Immunology Programme, Life Sciences Institute, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117456, Singapore.
3. Immunology Translational Research Program, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117597, Singapore.
4. NUS Centre for Cancer Research, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117599, Singapore.
5. Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117559, Singapore.
6. Department of Pharmacology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117559, Singapore.
7. National University Cancer Institute, Singapore 119074, Singapore.
#These authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Abstract
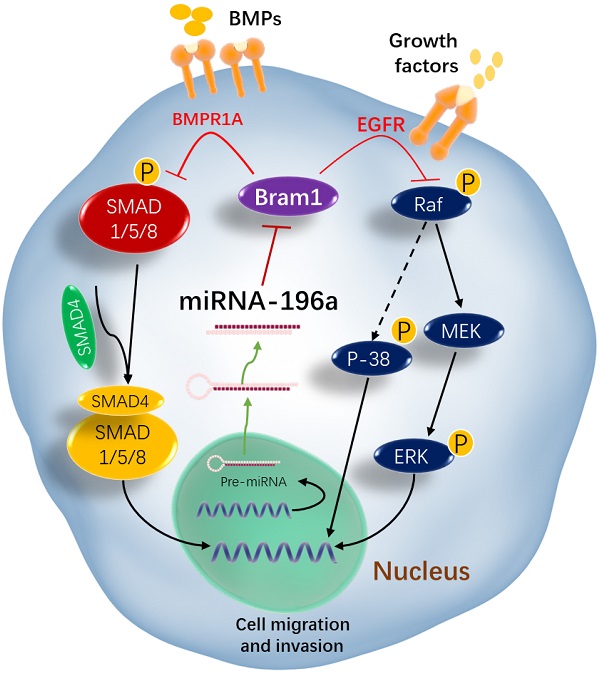
Rationale: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous ~22nt RNAs that play critical regulatory roles in various biological and pathological processes, including various cancers. Their function in renal cancer has not been fully elucidated. It has been reported that miR-196a can act as oncogenes or as tumor suppressors depending on their target genes. However, the molecular target for miR-196a and the underlying mechanism in miR-196a promoted cell migration and invasion in renal cancer is still not clear.
Methods: The expression, survival and correlation between miR-196a and BRAM1 were investigated using TCGA analysis and validated by RT-PCR and western blot. To visualize the effect of Bram1 on tumor metastasis in vivo, NOD-SCID gamma (NSG) mice were intravenously injected with RCC4 cells (106 cells/mouse) or RCC4 overexpressing Bram1. In addition, cell proliferation assays, migration and invasion assays were performed to examine the role of miR-196a in renal cells in vitro. Furthermore, immunoprecipitation was done to explore the binding targets of Bram1.
Results: TCGA gene expression data from renal clear cell carcinoma patients showed a lower level of Bram1 expression in patients' specimens compared to adjacent normal tissues. Moreover, Kaplan‑Meier survival data clearly show that high expression of Bram1correlates to poor prognosis in renal carcinoma patients. Our mouse metastasis model confirmed that Bram1 overexpression resulted in an inhibition in tumor metastasis. Target-prediction analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that Bram1 is a direct target of miR-196a in renal cells. Further, our in vitro functional assays revealed that miR-196a promotes renal cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Rescue of Bram1 expression reversed miR-196a-induced cell migration. MiR-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration by directly targeting Bram1 and inhibits Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation and MAPK pathways through BMPR1A and EGFR.
Conclusions: Our findings thus provide a new mechanism on the oncogenic role of miR-196a and the tumor-suppressive role of Bram1 in renal cancer cells. Dysregulated miR-196a and Bram1 represent potential prognostic biomarkers and may have therapeutic applications in renal cancer.
Keywords: MicroRNA-196a, renal cancer, Bram1, migration and invasion, SMAD and MAPK pathways

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact