Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(9):3636-3652. doi:10.7150/ijbs.71870 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Daidzein Synergizes with Gefitinib to Induce ROS/JNK/c-Jun Activation and Inhibit EGFR-STAT/AKT/ERK Pathways to enhance Lung Adenocarcinoma cells chemosensitivity
1. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung 404, Taiwan
2. Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung 40705, Taiwan
3. Faculty of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
4. Laboratory of Exercise Biochemistry, University of Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan
5. Department of Biomedical Imaging & Radiological Science College of Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung 404, Taiwan
6. Department of Pathology, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
7. Department of Hematology and Oncology, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan
8. School of Medicine Tzu Chi University, 701, Section 3, Chung-Yang Road, Hualien 97004, Taiwan
9. Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
10. Cardiovascular and Mitochondrial Related Disease Research Center, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan
11. Department of Biological Science and Technology, China Medical University, Taichung 406, Taiwan
12. Ph.D. Program for Biotechnology Industry, China Medical University, Taichung 406, Taiwan
13. Center of General Education, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Tzu Chi University of Science and Technology, Hualien 970, Taiwan
14. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung 404, Taiwan
15. Department of Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung 413, Taiwan
*These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
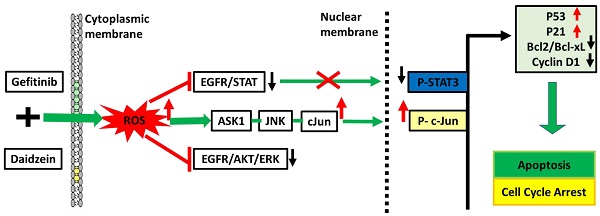
Lung cancer is the major cause of cancer associated mortality. Mutations in EGFR have been implicated in lung cancer pathogenesis. Gefitinib (GF) is a RTKI (receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor) first-choice drug for EGFR mutated advanced lung cancer. However, drug toxicity and cancer cell resistance lead to treatment failure. Consequently, new therapeutic strategies are urgently required. Therefore, this study was aimed at identifying tumor suppressive compounds that can synergistically improve Gefitinib chemosensitivity in the lung cancer treatment. Medicinal plants offer a vast platform for the development of novel anticancer agents. Daidzein (DZ) is an isoflavone compound extracted from soy plants and has been shown to possess many medicinal benefits. The anticancer potential of GF and DZ combination treatment was investigated using MTT, western blot, fluorescent microscopy imaging, flow cytometry and nude mice tumor xenograft techniques. Our results demonstrate that DZ synergistically induces c-Jun nuclear translocation through ROS/ASK1/JNK and downregulates EGFR-STAT/AKT/ERK pathways to activate apoptosis and a G0/G1 phase cell cycle blockade. In in-vivo, the combination treatment significantly suppressed A549 lung cancer cells tumor xenograft growth without noticeable toxicity. Daidzein supplements with current chemotherapeutic agents may well be an alternative strategy to improve the treatment efficacy of lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Chemosensitivity, Daidzein, ROS, Synergistic, c-Jun, Apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact